Gyrocompass and Magnetic compass are the two of the most important navigational instruments onboard ships. However, these instruments are not immune to errors and inaccuracies, which can lead to potentially dangerous situations if not addressed promptly. In this blog we will discuss the procedure on how to calculate both gyro and magnetic compass error, as well as the compass deviation. There are other ways to find compass error (such as transit bearings) but for this example we will use the most common method which is finding the azimuth of celestial body.
The Azimuth method.
The Azimuth method is a way of determining gyro error by taking bearings of celestial bodies at known azimuths. The method involves taking bearings of celestial bodies at known azimuths and comparing them with the bearings obtained from the ship’s compass. The difference between the two bearings gives the gyro error. Below is the following procedure.
Prepare the following information:
- Ships Gyro Heading and Magnetic Heading
- Gyrocompass and magnetic bearing of celestial body (i.e. sun). Use gyrocompass repeater with azimuth circle to get the gyro compass bearing. (Note: After getting the gyro bearing, you can easily get the magnetic bearing by applying the difference between gyro and magnetic heading)
- The latitude and longitude of the ship (GPS)
- Time in UTC
- Variation of the area (from chart or you can get it from GPS unit also)
- Scientific calculator
Get the latest Nautical Almanac
- Take note the value GHA (based on the current date and hour)
- Take note the declination value (Dec)
- d’ correction (can be found at the bottom of the page)
- Increments value in the increments table (based on the minutes of the time in UTC)
- d’ correction equivalent value (same page with the increments table)
Calculation
- If, Long East, LHA = GHA + LONG (- 360° as necessary)
- If, Long West, LHA = GHA – LONG (+ 360° as necessary)
- p = LHA; (360-LHA, if LHA is more than 180°)
A,B,and C values
- A=tan Latitude / tan p; (same name with Latitude only if LHA is between 90-270°, otherwise, it will be opposite name with latitude.)
- B = sin declination / tan p; (same name as declination)
- C= A+- B; (add if A and B are same name, subtract if different name; and name will follow to the bigger values).
Find the True Azimuth value
Find first the azimuth angle.
- tan azimuth angle (Zn) = 1 / (C x cos latitude); (Naming will depend on what quadrant is the value of your gyro bearing. For example, if your gyro bearing is 125° which is in the second quadrant and your azimuth angle is 30°, then the naming will look like this, S30E. Refer to the below diagram.
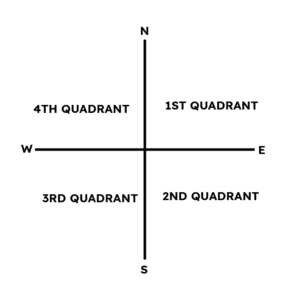
1st quadrant : N _E
2nd quadrant : S_E
3rd quadrant : S_W
4th quadrant : N_W
Let say if the Zn = S30°E, then the diagram will look like this.
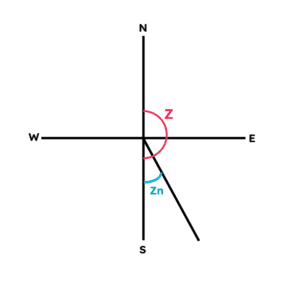
Then, in this example the True Azimuth (Z) = 150°.
Compare True Azimuth (Z) to Gyro bearing to get the Gyro Error
Gyro Error = Z-Gyro bearing; (Name low if gyro bearing is less than True azimuth and high if gyro bearing is greater than the true azimuth.)
Compare the True azimuth to Magnetic bearing to get the Magnetic Error(ME)
- ME = True azimuth – Magnetic bearing ; (Name the error W if Magnetic bearing is more than true azimuth, otherwise it is name E.)
Compare Magnetic error to Variation to get the Deviation
- Make the name of variation opposite (i.e. if it is 5°W make it 5°E)
- Deviation = Magnetic Error +- Variation; (add if same name or subtract if different name, then deviation name will the bigger value.)
Now you know the step-by-step procedure, you need to constant practice so that you can do it easily. You can download the Compass Error and Deviation Calculation Sheet below.